INFRARED THERMAL IMAGING
Infrared Thermal Imaging

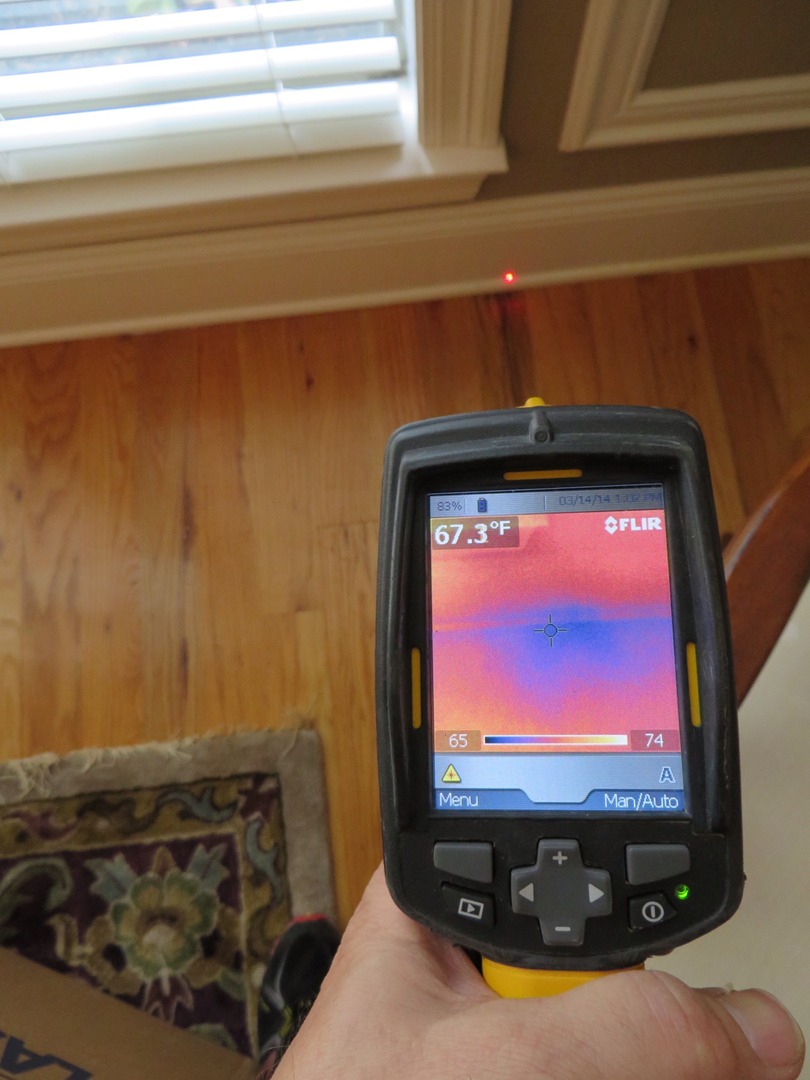
Thermography is the use of an infrared imaging and measurement camera to "see" and "measure" thermal energy emitted from an object. Thermal, or infrared energy, is light that is not visible because its wavelength is too long to be detected by the human eye; it's the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that we perceive as heat. Unlike visible light, in the infrared world, everything with a temperature above absolute zero emits heat. Even very cold objects, like ice cubes, emit infrared. The higher the object's temperature, the greater the IR radiation emitted. Infrared allows us to see what our eyes cannot. Infrared thermography cameras produce images of invisible infrared or "heat" radiation and provide precise non-contact temperature measurement capabilities. Nearly everything gets hot before it fails, making infrared cameras extremely cost-effective, valuable diagnostic tools in many diverse applications. And as industry strives to improve manufacturing efficiencies, manage energy, improve product quality, and enhance worker safety, new applications for infrared cameras continually emerge.
High definition (or high resolution) thermal imaging refers to the fine detail and clarity of a thermal image. This means it contains a large number of pixels per unit of area. In this case, a thermal imaging camera taking a high definition photo means you will find smaller problems at greater distances. You can find significant problems that could be missed with a lower resolution thermal imaging camera. More pixels mean greater temperature measurement accuracy, particularly for small objects. To the professional thermographer, a high definition thermal imager means a strong competitive advantage.
Our new high definition thermal imager saves us plenty of capture and reporting time. Moisture in building materials can destroy structural integrity and nurture mold. The first step in moisture problem remediation is to quickly and accurately locate and remove all sources of moisture. Infrared cameras instantly show you what's wet and what's dry. IR cameras can instantly find the ultimate source with little or no physical disassembly of the premises and minimal disturbance of inhabitants. Infrared cameras are the inspection assets preferred by building experts for fast, reliable, accurate building diagnosis in the entire range of building problems.
Infrared inspection is a powerful noninvasive method to monitor and diagnose the condition of buildings. Quickly identify problem areas that can't be seen by the naked eye - eliminating destructive probing methods. Results are captured and documented instantly and easily into professional reports - providing tangible proof of your findings
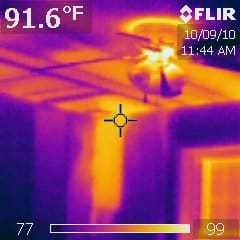
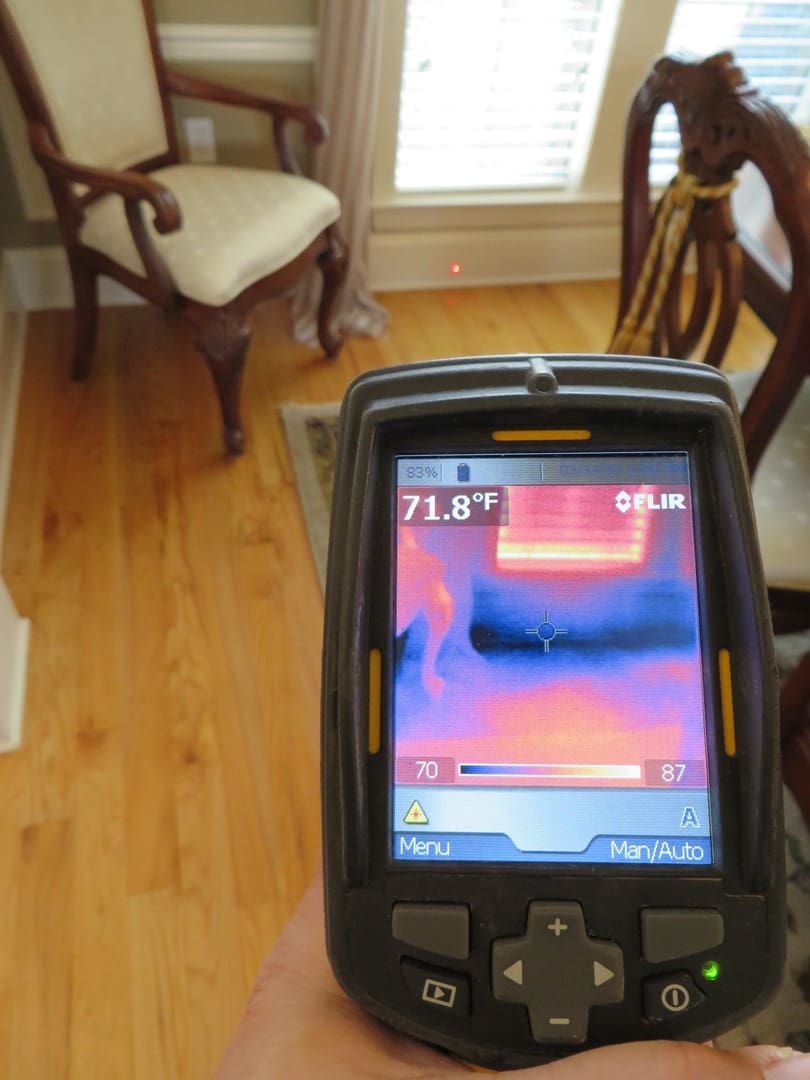
Detecting construction faults
Using thermal imaging, heat losses, humidity and air leaks in buildings become instantly visible, providing clear evidence of construction faults.
Detecting air leaks
Infrared thermography provides the most rapid means by which to identify unintentional air leakage pathways in a building envelope, although it cannot quantify the leakage rate.The benefits of employing infrared thermography in buildings are:
a. Air leakage pathways present within a completed construction can be identified and rectified prior to subjecting the building to air permeability tests, reducing the risk of repeat testing being required.
b. Depending upon the nature of the construction, even a building that meets or exceeds the building regulations may still be at risk of premature deterioration due to air leakage and subsequent condensation, therefore identifying where air leakage is occurring can be critical.
c. Air leakage pathways can often indicate rainwater ingress pathways further adding to the potential benefits of an infrared survey.
Thermography is commonly used to identify air change rates with the help of the so-called ‘blower-door’ process, which creates under-pressure in buildings. Because the air pressure outside is higher than the pressure inside, the air will try to enter through unsealed areas. Using an infrared camera, this airflow can easily be seen, clearly revealing any unsealed areas, which can then be attended to before coverings and fittings make correcting this potential fault both expensive and time-consuming.

Important Areas to Check
- in the kitchen around the sink, under the dishwasher, behind the refrigerator, and under the cooking range, as well as around vents and exhaust fans;
- in bathrooms around plumbing fixtures and outlets, shower and bathtub enclosures, fixtures and vents, the toilet and bidet, and windows;
- the HVAC system;
- the water heater;
- in the attic, including roof pass-throughs and penetrations, connecting walls, vents and fans, and recessed lights;
- in the basement, including walls, ductwork and crawlspaces;
- in the laundry area around the washer and dryer hookups, drip pans and exhaust vents, as well as utility sinks.
Infrared cameras are popular for finding moisture intrusion problems because of the many advantages they provide over conventional methods. Using an IR camera in conjunction with a moisture meter allows problem areas to be located quickly and documented easily.
all american home inspections, llc infrared thermal imaging inspection
infrared thermal imaging inspection in mandeville


